Discovering Minor Cannabinoids: Unlocking the Hidden Potential of Medical Cannabis
Medical cannabis has evolved beyond THC and CBD. Today, researchers are uncovering the power of minor cannabinoids—including CBN, CBG, CBC, and THCV—for supporting sleep, pain relief, mood, inflammation, and more.
Let’s explore these compounds and how they relate to the broader cannabis ecosystem through the Cannabinoid Family Tree, starting from CBGA, the “mother cannabinoid.”
🌱 Cannabinoid Family Tree
All cannabinoids begin as CBGA (Cannabigerolic Acid). Through heat, time, or oxidation, CBGA transforms into both major and minor cannabinoids—each offering unique therapeutic potential.
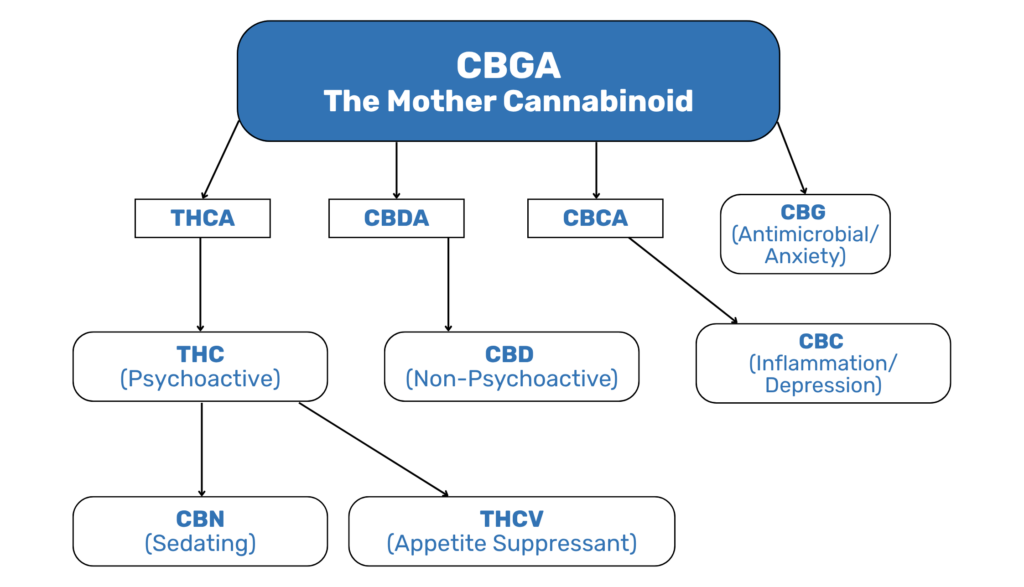
🧬 CBGA – The Mother of All Cannabinoids
CBGA is the chemical foundation of the cannabis plant. It converts into three key acidic cannabinoids:
- THCA → becomes THC
- CBDA → becomes CBD
- CBCA → becomes CBC
These changes occur during decarboxylation (heating) or through oxidation over time.
🔬 Research Insight: CBGA and its derivative, CBG, show promise as anti-inflammatory, antibacterial (especially against MRSA), and neuroprotective agents. (De Petrocellis et al., 2011)
🌟 Active Cannabinoids and Their Benefits
🔷 THCA → THC
THC (Tetrahydrocannabinol) is well-known for its psychoactive effects. However, it also:
- Reduces chronic pain
- Stimulates appetite
- Controls nausea and spasticity, particularly in cancer and MS patients
📘 Supported in studies like Whiting et al., 2015 (JAMA) and Health Canada’s clinical guidance documents.
🔷 THC → CBN
CBN (Cannabinol) forms when THC breaks down over time. It is mildly psychoactive and best known for:
- Sedative effects
- Potential neuroprotection
- Antibacterial action
🧪 In a study using ZTL-101 (THC/CBN/CBD blend), participants experienced improved sleep quality after 2 weeks. (Suraev et al., 2020)
🔷 THC → THCV
THCV (Tetrahydrocannabivarin) is a cannabinoid with distinct effects:
- May suppress appetite
- Supports blood sugar regulation
- Under investigation for Parkinson’s and psychosis
🧬 THCV interacts with CB1 and CB2 receptors and may improve insulin sensitivity, as seen in animal models. (Jadoon et al., 2016)
🟣 CBDA → CBD
CBD (Cannabidiol) is non-intoxicating and widely used to:
- Ease anxiety
- Manage epilepsy and seizures
- Promotes homeostasis
📘 CBD has demonstrated efficacy in seizure reduction (e.g., Epidiolex) and is under study for anxiety, PTSD, and pain. (Blessing et al., 2015)
🟠 CBCA → CBC
CBC (Cannabichromene) is non-psychoactive and being studied for:
- Anti-inflammatory effects
- Potential antidepressant properties
- Relief from pain and swelling
🧪 Preclinical trials suggest CBC suppresses inflammation and may enhance mood. (DeLong et al., 2010)
🟩 CBGA (unconverted) → CBG
CBG (Cannabigerol) forms directly from CBGA and supports:
- Pain and inflammation regulation
- Antibacterial resistance (including MRSA)
- Mood improvement and focus
🧠 In a 2021 survey of CBG users, 73% reported better outcomes for chronic pain, 78% for anxiety, and 80% for depression, often surpassing conventional medications. (Russo et al., 2021)
🧩 Why Minor Cannabinoids Matter
Despite their small quantities, minor cannabinoids are powerful therapeutic agents. When used together in full-spectrum or broad-spectrum cannabis formulations, they may work synergistically through the entourage effect.
🌿 Full-Spectrum Cannabis
Definition:
Full-spectrum products contain all naturally occurring compounds found in the cannabis plant, including:
- THC (tetrahydrocannabinol)
- CBD (cannabidiol)
- Minor cannabinoids (like CBN, CBG, CBC, THCV)
- Terpenes (aromatic compounds with therapeutic effects)
- Flavonoids and other plant materials
Key Benefit: This combination allows for the “entourage effect”—a synergistic interaction where cannabinoids and terpenes enhance each other’s therapeutic effects.
🌼 Broad-Spectrum Cannabis
Definition:
Broad-spectrum cannabis contains a wide range of cannabinoids and terpenes—but no detectable THC.
What it includes:
- CBD and other minor cannabinoids (CBG, CBC, etc.)
- Terpenes
- Flavonoids
What it excludes:
- THC is removed, typically during the extraction process.
Key Benefit: You still get some entourage effect benefits—without the risk of intoxication.
✅ Ready to Explore Minor Cannabinoids?
At Greenleaf Medical Clinic, our doctor will:
- Communicate directly with your referring physician
- Review your medical history thoroughly
- Check for any potential interactions with your current medications
- Recommend the most suitable form of cannabis (oil, capsule, dried flower, etc.)
- Create a personalized treatment plan with a dosing schedule and instructions
- Monitor your progress and adjust your plan as needed
Greenleaf is about safe, structured care — led by healthcare professionals who are committed to helping you reach your goals. Whether you’re new to cannabis or looking to refine your treatment, we’re here to support you every step of the way.
📚 Final Thought
Cannabis isn’t just about THC or CBD. Understanding the cannabinoid family tree empowers patients to make informed choices and unlock tailored symptom relief—whether for sleep, anxiety, pain, or metabolic health.
Start the process of becoming a patient with us by clicking here.



